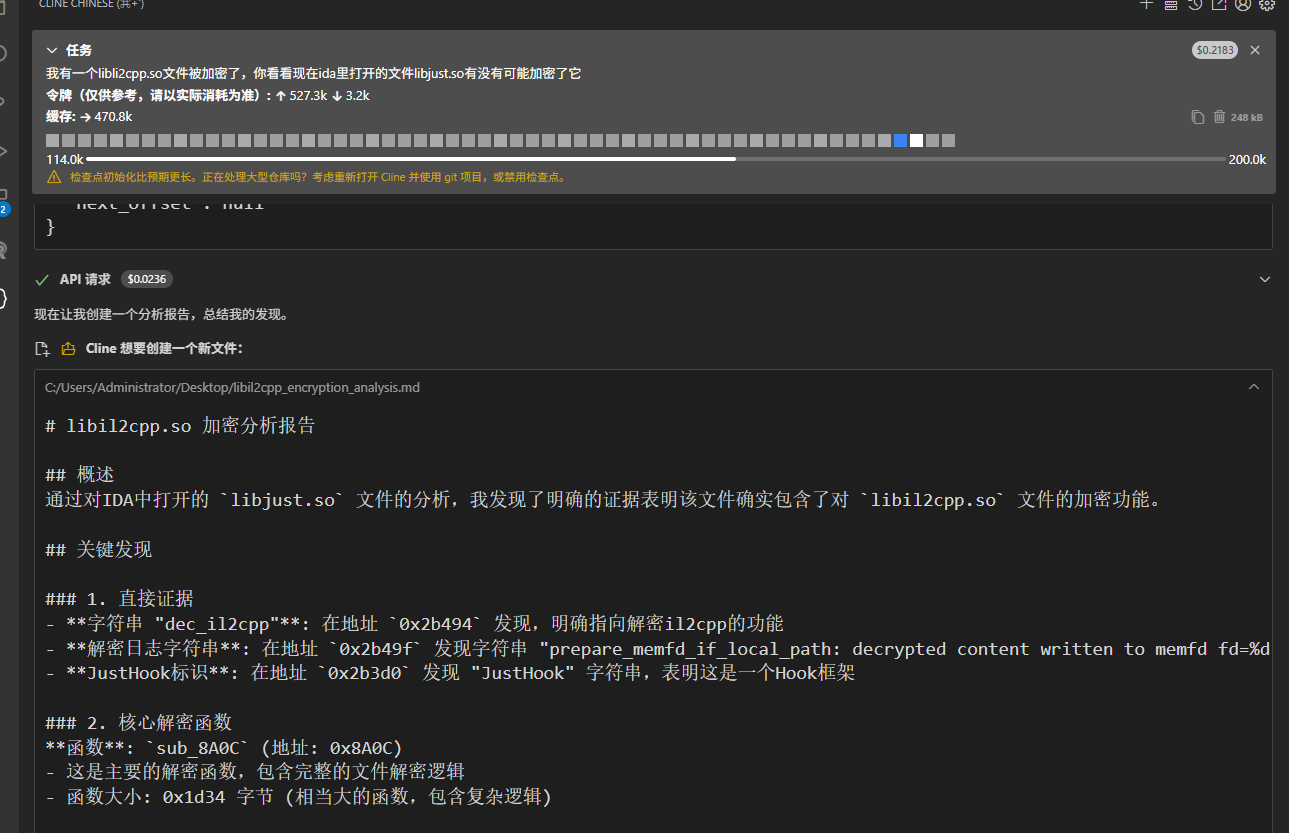
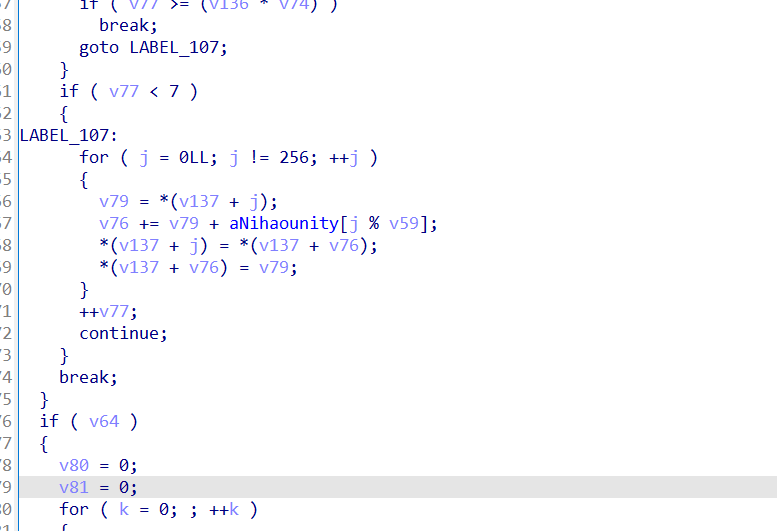
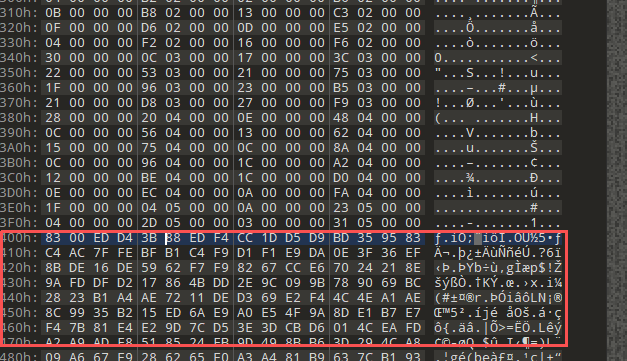
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
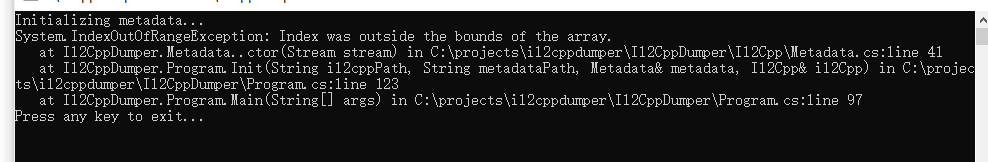
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
| # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import struct
UINT32_MASK = 0xFFFFFFFF
KEY = (0x12345678, 0x09101112, 0x13141516, 0x15161718)
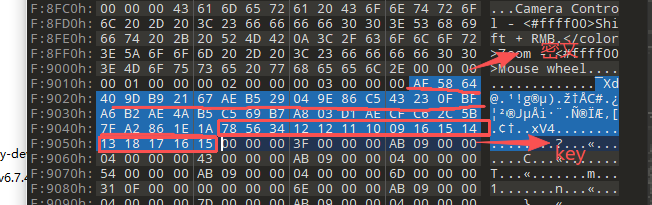
CIPHER_BYTES = bytes([
0xAF,0x58,0x64,0x40,0x9D,0xB9,0x21,0x67,
0xAE,0xB5,0x29,0x04,0x9E,0x86,0xC5,0x43,
0x23,0x0F,0xBF,0xA6,0xB2,0xAE,0x4A,0xB5,
0xC5,0x69,0xB7,0xA8,0x03,0xD1,0xAE,0xCF,
0xC6,0x2C,0x5B,0x7F,0xA2,0x86,0x1E,0x1A
])
def read_u32_le(buf, offset):
return struct.unpack_from("<I", buf, offset)[0]
def write_u32_le(bytearr, offset, value):
struct.pack_into("<I", bytearr, offset, value & UINT32_MASK)
def custom_tea_step(pair, key):
left, right = pair
delta = 0x61C88647
s = 0
# produce initial s = -delta*16 mod 2^32
for _ in range(16):
s = (s - delta) & UINT32_MASK
# 16 rounds: each round s += delta, then update right and left using subtraction-based ops
for _ in range(16):
s = (s + delta) & UINT32_MASK
t_right = (((left << 4) & UINT32_MASK) + key[2]) & UINT32_MASK
u_right = (left + s) & UINT32_MASK
v_right = (((left >> 5) & UINT32_MASK) + key[3]) & UINT32_MASK
right = (right - (t_right ^ u_right ^ v_right)) & UINT32_MASK
t_left = (((right << 4) & UINT32_MASK) + key[0]) & UINT32_MASK
u_left = (right + s) & UINT32_MASK
v_left = (((right >> 5) & UINT32_MASK) + key[1]) & UINT32_MASK
left = (left - (t_left ^ u_left ^ v_left)) & UINT32_MASK
return left, right
def decrypt_custom_mode(cipher_bytes, key):
b = bytearray(cipher_bytes) # operate on a mutable copy
# current state is the first two uint32 words (little-endian)
state_l = read_u32_le(b, 0)
state_r = read_u32_le(b, 4)
# process blocks in reverse order (offsets 32,24,16,8)
for off in (32, 24, 16, 8):
# xor cipher block with current state to produce plaintext for that block
c_l = read_u32_le(b, off)
c_r = read_u32_le(b, off + 4)
p_l = c_l ^ state_l
p_r = c_r ^ state_r
write_u32_le(b, off, p_l)
write_u32_le(b, off + 4, p_r)
# advance keystream/state by applying custom tea on the state
state_l, state_r = custom_tea_step((state_l, state_r), key)
# write the updated state back to the beginning (this mirrors the original)
write_u32_le(b, 0, state_l)
write_u32_le(b, 4, state_r)
# final state advancement and write-back (same as original algorithm)
state_l, state_r = custom_tea_step((state_l, state_r), key)
write_u32_le(b, 0, state_l)
write_u32_le(b, 4, state_r)
return bytes(b)
if __name__ == "__main__":
plaintext = decrypt_custom_mode(CIPHER_BYTES, KEY)
print("Decrypted (hex):", plaintext.hex())
try:
decoded = plaintext.decode("ascii")
print("Decrypted (ASCII):", decoded)
except UnicodeDecodeError:
printable = ''.join((chr(x) if 32 <= x < 127 else '.') for x in plaintext)
print("Decrypted (printable):", printable)
|
;)